Another thing I wanted to play with is Netbox and found a good article to follow. So credits to the authors.
Using my current ceos lab from https://github.com/thomarite/ceos-testing
I followed Rick’s article to install netbox-docker and his own repo with the nornir examples using netbox. In this case nornir is going to use netbox as inventory. Normally I use local files. I created a python venv for 3.7.3
mkdir netbox-example; cd netbox-example
pyenv local 3.7.3
python -m virtualenv venv
source venv/bin/activate
git clone https://github.com/netbox-community/netbox-docker.git
cd netbox-docker
vim docker-compose.yml --> so it always expose 8080
nginx:
...
ports:
- 8080:8080
docker-compose pull
docker-compose up
When installing the requirements for “nornir-napalm-netbox-demo” I had to modify the version of some packages. So I removed the required version and I left pip to install the latest. I didnt use the makefile.
git clone https://github.com/rickdonato/nornir-napalm-netbox-demo cd nornir-napalm-netbox-demo python -m pip install -r requirements.txt
I struggled quite a bit with the management IP in netbox and the meaning of “platform”
- Create Manufacturers under Device Types: I created “Arista”
- Create Device Types under Device Types: I created “ceos”
- Create Platforms under Devices: This is VERY important as it has to be a supported NAPALM platform!!! So for Arista, I need “eos”.
- Create Device Roles under Devices. I created “pe”
- Create Devices under Devices.
- Within each device: add a management interface. Here, I got confused as I was adding the interface in the inventory section. The inventory section is info to/from the device using NAPALM. So you need to go to the bottom of the page, add the interface
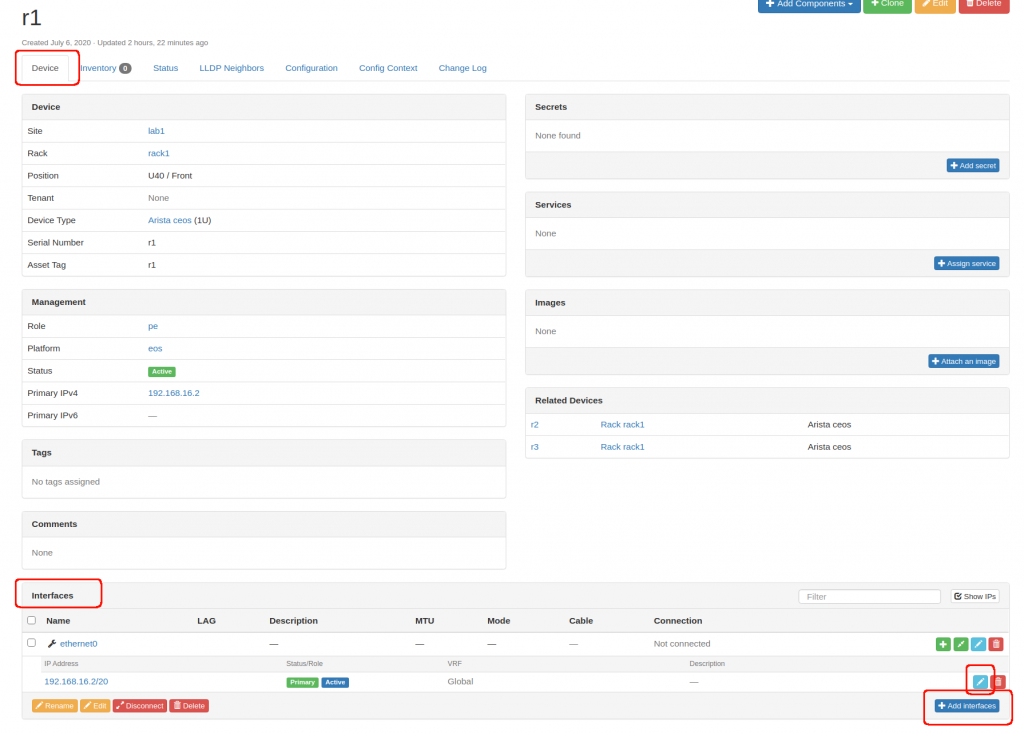
- and then add an IP to that interface and mark it as primary.
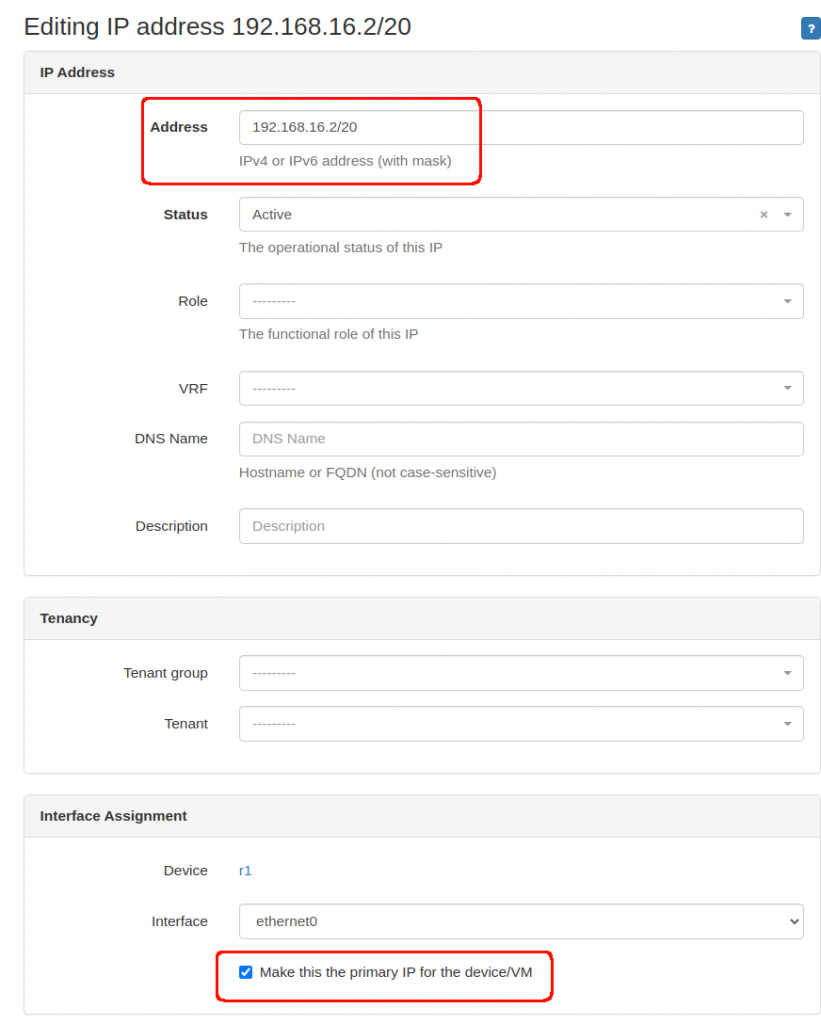
Keep in mind that initially, I was using “0.0.0.0” for each device as that’s the IP I have be using for all my scripts lately.
Keep in mind (II) that we are using docker twice (from different commands…) one to get netbox and the other via docker(-topo) to get the Arista ceos containers…. and we have iptables rules under the hood created by both…
But, let’s go step by step. Now we need to confirm that our nornir scrip can connect to netbox. So follow “Nornir-to-Netbox Configuration” section. This is my file. I updated the nb_url and nb_token. Notice the usage of “transform_function“.
--- core: num_workers: 20 inventory: plugin: nornir.plugins.inventory.netbox.NBInventory options: nb_url: 'http://0.0.0.0:8080' nb_token: '<NETBOX_API_TOKEN>' ssl_verify: False transform_function: "helpers.adapt_user_password"
You need to update “scripts/secrets.py” with the devices you have in your inventory and the user/pass:
creds = {
"r1": {"username": "user", "password": "pas123"},
"r2": {"username": "user", "password": "pas123"},
"r3": {"username": "user", "password": "pas123"},
}
So now we can test if nornir can connect to netbox:
/netbox-example/nornir-napalm-netbox-demo master$ python scripts/helpers.py --inventory
{'defaults': {'connection_options': {},
'data': {},
'hostname': None,
'password': None,
'platform': None,
'port': None,
'username': None},
'groups': {},
'hosts': {'r1': {'connection_options': {},
'data': {'asset_tag': 'r1',
'model': 'ceos',
'role': 'pe',
'serial': 'r1',
'site': 'lab1',
'vendor': 'Arista'},
'groups': [],
'hostname': '192.168.16.2',
'password': 'pas123',
'platform': 'eos',
'port': None,
'username': 'user'},
'r2': {'connection_options': {},
'data': {'asset_tag': 'r2',
'model': 'ceos',
'role': 'pe',
'serial': 'r2',
'site': 'lab1',
'vendor': 'Arista'},
'groups': [],
'hostname': '192.168.16.3',
'password': 'pas123',
'platform': 'eos',
'port': None,
'username': 'user'},
'r3': {'connection_options': {},
'data': {'asset_tag': 'r3',
'model': 'ceos',
'role': 'pe',
'serial': 'r3',
'site': 'lab1',
'vendor': 'Arista'},
'groups': [],
'hostname': '192.168.16.4',
'password': 'pas123',
'platform': 'eos',
'port': None,
'username': 'user'}}}
All good. Let’s see if we can get backups from the devices.
netbox-example/nornir-napalm-netbox-demo master$ python scripts/backup_configs.py Backup Device configurations** r1 ** changed : True * vvvv Backup Device configurations ** changed : False vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv INFO ---- napalm_get ** changed : False --------------------------------------------- INFO ---- write_file ** changed : True ---------------------------------------------- INFO ^^^^ END Backup Device configurations ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ r2 ** changed : True * vvvv Backup Device configurations ** changed : False vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv INFO ---- napalm_get ** changed : False --------------------------------------------- INFO ---- write_file ** changed : True ---------------------------------------------- INFO ^^^^ END Backup Device configurations ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ r3 ** changed : True * vvvv Backup Device configurations ** changed : False vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv INFO ---- napalm_get ** changed : False --------------------------------------------- INFO ---- write_file ** changed : True ---------------------------------------------- INFO ^^^^ END Backup Device configurations ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ (venv) /netbox-example/nornir-napalm-netbox-demo master$
Great all good.
Now, let’s see netbox using NAPALM. If you click on “Status” for any device, netbox will use NAPALM to get the facts from the device. If netbox is not configured properly with NAPALM, it will fail. This is a working scenario:
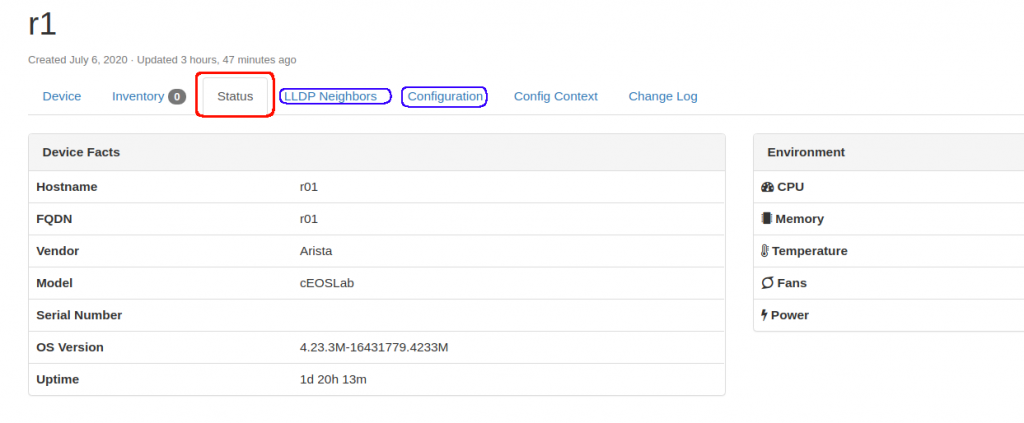
The tabs “LLDP neighbors” and “Configuration” relay too in NAPALM.
So for configuring netbox with napalm you need to tell netbox the user/pass that NAPALM needs:
netbox-example$ vim netbox-docker/env/netbox.env ... NAPALM_USERNAME=user NAPALM_PASSWORD=pas123 NAPALM_TIMEOUT=10 ...
Very likely you will have to restart netbox:
/netbox-docker release$ docker-compose down /netbox-docker release$ docker-compose up
As mentioned before, I had an issue when I was using “0.0.0.0” as IP. By default (as It seems I can’t think) I was using the exposed IP/port from docker-topo to reach the ceos switches. I haven’t had an issue until using netbox.
I am using docker for netbox and docker(-topo) for my arista cEOS switches. So the connectivity between netbox and ceos is via the IPs/interfaces/bridges created by docker. And remember… you have iptables under the hood. My first mistake was telling netbox to use 0.0.0.0 as it is the one I am using to testing from my scripts when connecting to ceos. Netbox needs to point to the IP assigned by docker :facepalm: 192.16.16.x in my case. Second one, the port, same thing docker exposes the port 443 as 900x for external connections and I use 900x in my scripts. From netbox point of view, it is still 443 :facepalm: And finally, I am calling docker twice for building my lab, one for netbox-docker and the other for ceos. You need to keep an eye on iptables changes when restarting netbox via docker-compose because you can be in the situation that netbox traffic is dropped in DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 :facepalm: (need to try to write a docker-compose to build everything in one go)
So when I was having errors from netbox that it was being rejected when connecting to ceos devices via NAPALM, I couldnt understand it. My scripts were fine using those details (0.0.0.0:900x)
I ran tcpdump on one ceos on the “ethernet0” interface and NOTHING was hitting the interface from netbox on port 900x but my scripts could…..
Somehow netbox wasnt able to reach ceos r1??? In my head, netbox and ceos devices were all in 0.0.0.0….. so no routing, no firewalls, they are connected in the same network 0.0.0.0…..
At the end I waked up and realised that the docker devices are using the IPs provided by docker so it is following normal routing… and firewalling by iptables. The same for ceos devices, they have IPs (different from 0.0.0.0)
So I updated netbox with the correct management IPs for r1, r2 and r3 ceos.
When I filtered by the real netbox IP in r1 tcpdump ethernet0, I was seeing traffic on 900x!!! Good. Then I realised that it has to be 443. So I removed my hack to update the port to 900x.
For a different reason I had to restart docker-topo (for ceos) and then docker netbox. And now, I coudnt see any traffic from netbox in r1….. I “didn’t” change anything. So the routing didnt change, there was something else “cutting” the connection: iptables
docker uses iptables very heavily. I realised that after restart docker-netbox, iptables changed…
before restart:
# iptables -t filter -S DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 Warning: iptables-legacy tables present, use iptables-legacy to see them -N DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -j ACCEPT -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i br-94a8183a4fb1 ! -o br-94a8183a4fb1 -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i br-0d4ec9aba9bd ! -o br-0d4ec9aba9bd -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i br-609619313dc8 ! -o br-609619313dc8 -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i br-61d32350cb58 ! -o br-61d32350cb58 -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i br-384488acbc99 ! -o br-384488acbc99 -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i docker0 ! -o docker0 -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -j RETURN
after restart:
# iptables -t filter -S DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 Warning: iptables-legacy tables present, use iptables-legacy to see them -N DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i br-381cdff63d2f ! -o br-381cdff63d2f -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -j ACCEPT -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i br-94a8183a4fb1 ! -o br-94a8183a4fb1 -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i br-0d4ec9aba9bd ! -o br-0d4ec9aba9bd -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i br-609619313dc8 ! -o br-609619313dc8 -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i br-61d32350cb58 ! -o br-61d32350cb58 -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i docker0 ! -o docker0 -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -j RETURN
With the restart, docker created a new bridge interface for netbox (old: br-384488acbc99, new: br-381cdff63d2f) and it wasnt hitting anymore the “DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -j ACCEPT”
So I had to make an iptables change:
# iptables -t filter -D DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -j ACCEPT # iptables -t filter -I DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -j ACCEPT # iptables -t filter -S DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 Warning: iptables-legacy tables present, use iptables-legacy to see them -N DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -j ACCEPT -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i br-381cdff63d2f ! -o br-381cdff63d2f -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i br-94a8183a4fb1 ! -o br-94a8183a4fb1 -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i br-0d4ec9aba9bd ! -o br-0d4ec9aba9bd -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i br-609619313dc8 ! -o br-609619313dc8 -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i br-61d32350cb58 ! -o br-61d32350cb58 -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -i docker0 ! -o docker0 -j DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 -A DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 -j RETURN #
And finally, netbox could use napalm to contact the ceos devices…. Calling docker twice is not a great idea….
BTW, this is my docker ps with netbox and ceos devices:
(venv) /netbox-example$ docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES c23be76ffd54 nginx:1.17-alpine "nginx -c /etc/netbo…" 4 hours ago Up 4 hours 80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8080->8080/tcp netbox-docker_nginx_1 5a0b89f18578 netboxcommunity/netbox:latest "/opt/netbox/docker-…" 4 hours ago Up 4 hours netbox-docker_netbox_1 528948de329b netboxcommunity/netbox:latest "python3 /opt/netbox…" 4 hours ago Up 4 hours netbox-docker_netbox-worker_1 29529302ba1c redis:5-alpine "docker-entrypoint.s…" 4 hours ago Up 4 hours 6379/tcp netbox-docker_redis_1 5e975ec2aa70 redis:5-alpine "docker-entrypoint.s…" 4 hours ago Up 4 hours 6379/tcp netbox-docker_redis-cache_1 6158672a4ae6 postgres:11-alpine "docker-entrypoint.s…" 4 hours ago Up 4 hours 5432/tcp netbox-docker_postgres_1 34841aa098d4 ceos-lab:4.23.3M "/sbin/init systemd.…" 5 hours ago Up 5 hours 0.0.0.0:2002->22/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9002->443/tcp 3node_r03 4ca92c6a3b09 ceos-lab:4.23.3M "/sbin/init systemd.…" 5 hours ago Up 5 hours 0.0.0.0:2001->22/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9001->443/tcp 3node_r02 67e8b7ab84e0 ceos-lab:4.23.3M "/sbin/init systemd.…" 5 hours ago Up 5 hours 0.0.0.0:2000->22/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9000->443/tcp 3node_r01
I was painful but I learned a couple of things about netbox, nornir and docker/iptables!!!